Definition of Phylogeny
Phylogeny refers to the evolutionary history and relationships among organisms. It is the study of how species are related to each other through common ancestors. Phylogenetic analysis uses various methods to construct evolutionary trees that depict these relationships.
Importance of Studying Bird Phylogeny
Understanding bird phylogeny is crucial for several reasons:
- Evolutionary Relationships: Studying bird phylogeny helps scientists understand how different bird species are related and how their characteristics have evolved over time. This information provides insights into the origins and diversification of bird species.
- Conservation Efforts: Knowledge of bird phylogeny can aid in conservation efforts by identifying endangered species and understanding their unique evolutionary history. This information helps prioritize conservation efforts and protect biodiversity.
- Ecological Studies: Studying bird phylogeny allows researchers to examine the evolution of different ecological traits and behaviors. This knowledge helps in understanding various aspects of bird biology, including migration patterns, feeding habits, and reproductive strategies.
- Medical Research: Bird phylogeny provides a framework for studying avian diseases and their potential transmission to humans. By understanding the evolutionary relationships between birds, scientists can better predict disease risks and develop effective prevention strategies.
In conclusion, studying bird phylogeny is essential for understanding evolutionary relationships, guiding conservation efforts, exploring ecological traits, and conducting medical research. It provides a foundation for further scientific discoveries and a deeper understanding of the avian world.
Evolutionary History of Birds
Origin of Birds
The origin of birds can be traced back to the late Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. Birds are believed to have evolved from a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs, which also includes famous dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptors. This evolutionary transition from dinosaurs to birds is supported by fossil evidence, such as the discovery of Archaeopteryx, an ancient bird-like dinosaur with feathered wings.
Early Bird Evolution
After the origin of birds, they underwent a process of diversification and evolution. During this time, various bird groups emerged, each with its unique characteristics. One significant development in bird evolution was the development of flight feathers, which allowed birds to fly. This adaptation enabled birds to occupy different ecological niches and expand their habitats.
Furthermore, the evolution of a lightweight skeleton, beak adaptions, and highly efficient respiratory and circulatory systems contributed to the success of birds. These adaptations allowed birds to exploit various food sources, migrate over long distances, and develop complex social behaviors.
In conclusion, the evolutionary history of birds traces back to the late Jurassic period, with birds evolving from theropod dinosaurs. Birds have undergone significant changes and adaptations, including the development of flight feathers and various anatomical modifications. Understanding the early bird evolution provides insights into how birds have become the diverse and successful group of animals we see today.
Evolutionary History of Birds
Origin of Birds
The origin of birds can be traced back to the late Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. Birds evolved from a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs, supported by fossil evidence like Archaeopteryx, an ancient bird-like dinosaur with feathered wings.
Early Bird Evolution
After their origin, birds underwent diversification and evolution. They developed flight feathers, allowing them to fly and occupy different ecological niches. Lightweight skeletons, beak adaptations, and efficient respiratory and circulatory systems contributed to their success in exploiting food sources, migrating long distances, and developing complex social behaviors.
Classification of Birds
Orders and Families of Birds
Birds are classified into various orders and families based on their anatomical characteristics, behavior, and genetic relationships. Some common orders include Passeriformes (songbirds), Falconiformes (birds of prey), and Charadriiformes (shorebirds). Each order consists of multiple families that share common traits.
Relationships between Bird Groups
Bird groups are related through evolutionary history and share common ancestry. They can be grouped into larger categories such as water birds, land birds, and flightless birds. The relationships between different bird groups are studied using genetic analysis, anatomical comparisons, and fossil records.
Understanding the classification and relationships between bird groups helps scientists study their evolutionary history, behavior, and ecological roles. It also provides valuable insights into their conservation and management.
Molecular Phylogeny of Birds
DNA Sequencing Techniques
DNA sequencing techniques have revolutionized our understanding of bird phylogeny and evolution. Scientists can now analyze the genetic material of different bird species to determine their relationships and genetic similarities. By sequencing specific regions of DNA, such as mitochondrial DNA or nuclear genes, researchers can compare sequences and identify patterns of genetic variation. These techniques provide valuable insights into the evolutionary history and relatedness of bird species.
Molecular Clocks and Dating Bird Evolution
Molecular clocks are used to estimate the timing of evolutionary events by measuring the rate of genetic mutations over time. By comparing DNA sequences between different species, scientists can calculate the approximate time when these species diverged from a common ancestor. Molecular clocks have been used to estimate the age of major bird lineages and the timing of important evolutionary events, such as the transition from flightlessness to flight in certain bird groups. These dating techniques help us understand the timeline of bird evolution and how different bird species have adapted and diversified over millions of years.
In summary, the field of molecular phylogeny has greatly enhanced our understanding of bird evolution. DNA sequencing techniques and molecular clocks have allowed scientists to uncover the relationships between different bird species and estimate the timing of key evolutionary events. This knowledge is crucial for studying the ecological roles of birds, their behavior, and for effective conservation and management strategies.

Morphological Characteristics and Phylogeny
Feathers and Flight Adaptations
Feathers play a crucial role in bird flight and have been key to the success and diversification of birds. Feathers are unique to birds and are highly modified scales that provide lightweight insulation and enable powered flight. Different bird species have varying feather structures and adaptations, such as specialized wing feathers for soaring or long tail feathers for maneuverability. These adaptations have allowed birds to occupy different ecological niches and thrive in diverse environments.
Skeletal Features and Bird Lineages
Bird skeletons also provide important clues about bird evolution and phylogeny. By studying skeletal features, scientists can categorize birds into different lineages based on their anatomical similarities and differences. For example, the presence or absence of a keeled sternum is a distinguishing feature that separates flightless birds from those capable of flight. Additionally, the structure of the beak, legs, and feet can reveal information about a bird’s diet and habitat.
Understanding the morphological characteristics of birds and their evolutionary history is crucial for our knowledge of biodiversity and conservation efforts. By combining molecular phylogeny with morphological studies, scientists can gain a comprehensive understanding of bird evolution and the factors that have shaped the amazing diversity of bird species we see today.
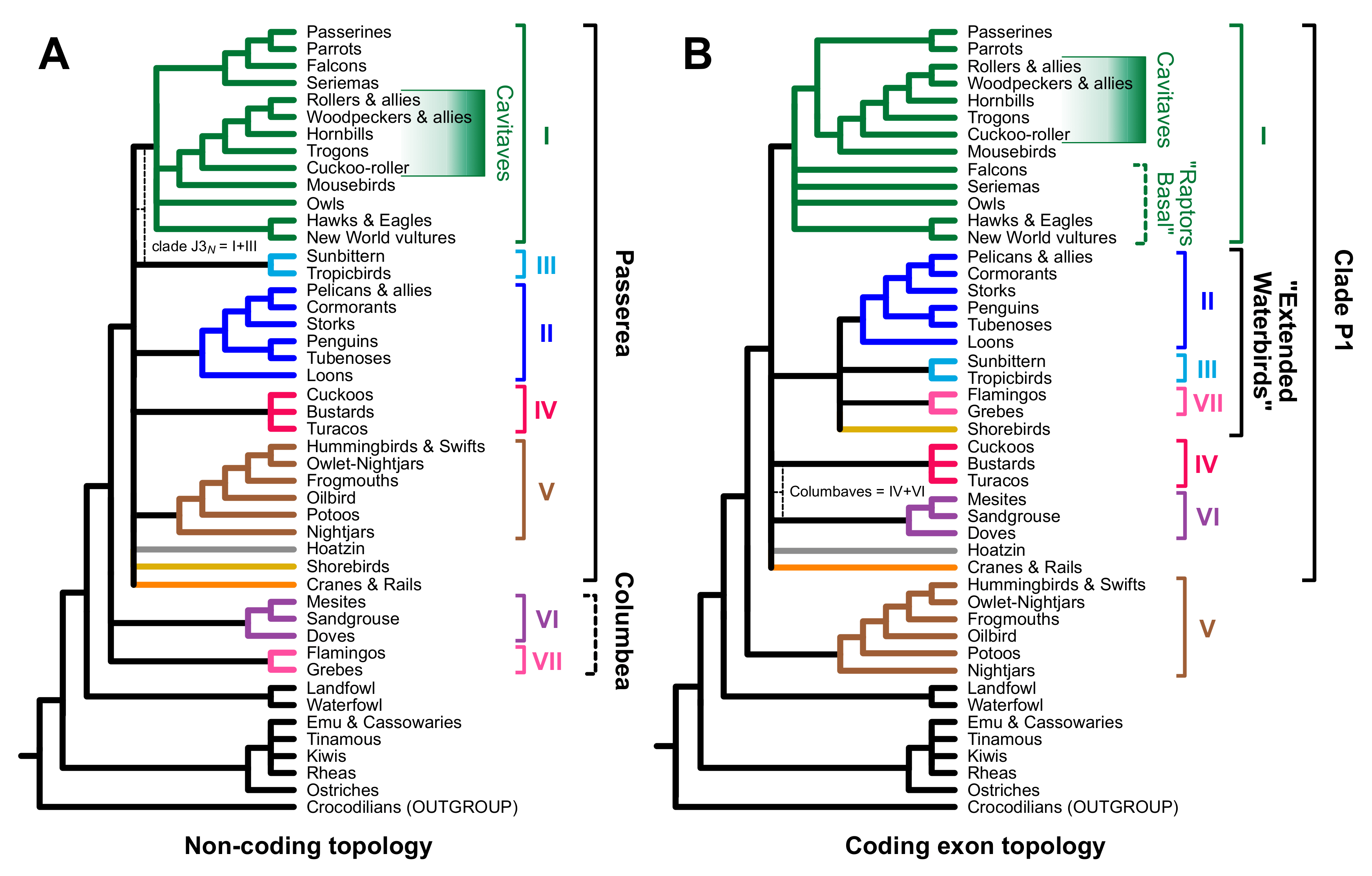
Phylogenetic Tree of Birds
Major Clades and Subclades
Birds are classified into several major clades and subclades based on their evolutionary relationships. These groupings help us understand the diversification of birds and their shared ancestry. Some of the major clades include:
- Paleognathae: This group includes flightless birds like ostriches and emus, as well as the ancient kiwis and tinamous.
- Neognathae: This is the largest clade of birds and includes most modern bird species. It is further divided into several subclades, such as Galloanserae (ducks, geese, and chickens) and Neoaves (all other birds).
Within these major clades, there are numerous subclades that represent more specific groups of birds, each with their own distinctive characteristics and ecological roles. These subclades have diversified over millions of years, adapting to different habitats and lifestyles.
Relationships between Modern Bird Groups
The relationships between modern bird groups can be mapped on a phylogenetic tree, which shows the evolutionary connections between different species. Advances in molecular genetics have allowed scientists to construct increasingly accurate phylogenetic trees for birds.
Based on these trees, we can see that certain bird groups are more closely related to each other than others. For example, passerines (songbirds) are a highly diverse group that make up approximately half of all bird species and have evolved many specialized adaptations for different habitats.
Understanding the relationships between modern bird groups helps us understand their shared evolutionary history and can provide insights into their ecological roles and conservation needs.
By studying the morphological characteristics of birds and their phylogeny, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the diversity and evolutionary processes that have shaped the avian world. This knowledge is essential for effective conservation strategies and safeguarding the rich biodiversity of bird species.
Factors Affecting Bird Speciation
Geographic Isolation
Geographic isolation plays a crucial role in bird speciation. When populations of birds become separated by physical barriers like mountains, oceans, or other geographical features, they are unable to interbreed. Over time, this isolation leads to the accumulation of genetic differences, ultimately resulting in the formation of new species.
Ecological Factors
Ecological factors also contribute to bird speciation. Different habitats and environments impose varying selective pressures on birds, leading to adaptations that enhance their survival and reproduction. As birds adapt to different ecological niches, they may diverge genetically and morphologically, resulting in the formation of new species.
Understanding the factors influencing bird speciation is essential for conserving their biodiversity. By identifying and protecting areas that promote speciation, such as ecologically diverse habitats and regions with high levels of geographic isolation, we can help ensure the long-term survival of bird species. Additionally, studying the factors driving speciation can provide valuable insights into the processes that shape the evolution of bird populations, enhancing our understanding of the natural world.

Factors Affecting Bird Speciation
Geographic Isolation
Geographic isolation plays a crucial role in bird speciation. When populations of birds become separated by physical barriers like mountains, oceans, or other geographical features, they are unable to interbreed. Over time, this isolation leads to the accumulation of genetic differences, ultimately resulting in the formation of new species.
Ecological Factors
Ecological factors also contribute to bird speciation. Different habitats and environments impose varying selective pressures on birds, leading to adaptations that enhance their survival and reproduction. As birds adapt to different ecological niches, they may diverge genetically and morphologically, resulting in the formation of new species.
Recent Discoveries and Research on Bird Phylogeny
Fossil Discoveries
Recent fossil discoveries have provided valuable insights into the evolutionary history and phylogeny of birds. Fossils can help researchers understand how different bird species are related and how they have evolved over time. By examining the structure and characteristics of these ancient remains, scientists can reconstruct the branches of the bird family tree and uncover important evolutionary relationships.
Genetic Studies
Advancements in genetic research have revolutionized our understanding of bird phylogeny. DNA analysis allows scientists to compare the genetic sequences of different bird species, providing evidence for their evolutionary relationships. By studying the similarities and differences in their genomes, researchers can track the divergence of bird lineages and gain a deeper understanding of their evolutionary history.
Understanding the factors influencing bird speciation, along with the recent discoveries and research on bird phylogeny, is essential for comprehending the complex processes that drive the evolution and diversification of bird populations. By combining knowledge about geographic isolation, ecological factors, fossil evidence, and genetic studies, scientists can continue to unravel the mysteries of bird speciation and contribute to the conservation of their biodiversity.
Factors Affecting Bird Speciation
Geographic Isolation
Geographic isolation plays a crucial role in the speciation of birds. When populations of birds become separated by physical barriers such as mountains or oceans, they are unable to interbreed. This leads to the accumulation of genetic differences over time, ultimately resulting in the formation of new species.
Ecological Factors
Ecological factors also contribute to bird speciation. Different habitats and environments impose varying selective pressures on birds, leading to adaptations that enhance their survival and reproduction. As birds adapt to different ecological niches, they may diverge genetically and morphologically, resulting in the formation of new species.
Recent Discoveries and Research on Bird Phylogeny
Fossil Discoveries
Recent fossil discoveries have provided valuable insights into the evolutionary history and phylogeny of birds. By examining the structure and characteristics of ancient remains, scientists can reconstruct the branches of the bird family tree and uncover important evolutionary relationships.
Genetic Studies
Advancements in genetic research have revolutionized our understanding of bird phylogeny. DNA analysis allows scientists to compare the genetic sequences of different bird species, providing evidence for their evolutionary relationships. By studying the similarities and differences in their genomes, researchers can track the divergence of bird lineages and gain a deeper understanding of their evolutionary history.
Conclusion
Significance of Understanding Bird Phylogeny
Understanding the factors influencing bird speciation, as well as recent discoveries and research on bird phylogeny, is crucial for comprehending the complex processes that drive the evolution and diversification of bird populations. It helps us gain insight into the diversity of bird species and their ecological adaptations.
Future Directions in Bird Phylogeny Research
Future research on bird phylogeny should continue to explore new fossil discoveries and advancements in genetic analysis. By integrating multiple lines of evidence, researchers can further refine our understanding of bird evolution and uncover additional insights into their phylogenetic relationships. This knowledge is essential for conserving the biodiversity of bird species and informing conservation efforts.
Overall, the study of bird speciation and phylogeny provides a fascinating glimpse into the intricate mechanisms of evolution and highlights the importance of preserving the rich variety of bird life on our planet.